NEW! Lead Hazard Reduction Program
In partnership with U.S. Housing and Urban Development, Two Rivers received a grant to perform lead testing and abatement to qualifying families within our district.
Our certified Lead Hazard Risk Assessors will use multiple methods to test for lead in and around your home. If lead is found, TRPHD will hire trained contractors to perform necessary repairs (abatement), leading to a safer home for all. In addition, TRPHD will also assess your home for other environmental factors, like mold, pests, and radon. Funding is also available to ease these problems as well.
Homeowners, renters, and landlords can all qualify for this program! The requirements are as follows. If you believe you meet these criteria, please fill out the link below or contact Ashley Green (agreen@trphd.ne.gov) for more information/paper application.
Homeowners
-
House must be built before 1978
-
Must have proof of ownership
-
A child under 6 must reside in the home over 75% of the time
-
Household income must be at or below 80% of the median area income by county
Landlords and Rental tenants
-
Tenants must have a child under 6 residing in the home over 75% of the time and be at or below 80% of the median area income (by county)
-
Landlords must have proof of ownership, intend to rent the unit to families in future leases, and be able to contribute a 10% match of all repairs performed in the unit.
-
Landlord and tenants MUST both agree to participate in the program and meet the qualifications below.
Fill out our screening form here and a member of the program staff will be in contact with you shortly!
Trusted Resources
What is Lead?
Lead is a naturally occurring bluish-gray metal found in small amounts in the earth's crust. Lead is mined and then used in products to make them durable and last longer. Once lead is used in a product, it is nearly impossible to identify with the naked eye. Lead does not biodegrade or disappear from the environment over time.
Health Effects of Lead
Lead is a neurotoxin to humans and animals. When taken in via ingestion or inhalation it can cause lead poisoning. Lead poisoning can cause a variety of permanent health issues.
In children it can cause:
- Behavioral and learning problems
- Lower IQ and hyperactivity
- Slowed growth
- Hearing problems
- Anemia
In adults it can lead to:
- Nerve disorders
- Increased blood pressure
- Decreased kidney function
- Reproductive problems
- Memory and concentration problems
Where Lead Can be Found
| pre-1978 homes | old toys or furniture | glazed or painted dishware | |
| cracking or peeling paint | antiques | ceramics | |
| contaminated soil | construction materials | cosmetics | |
| contaminated dust | bullets or ammunition | shooting ranges | |
| drinking water | some herbal or home remedies | fishing weights | |
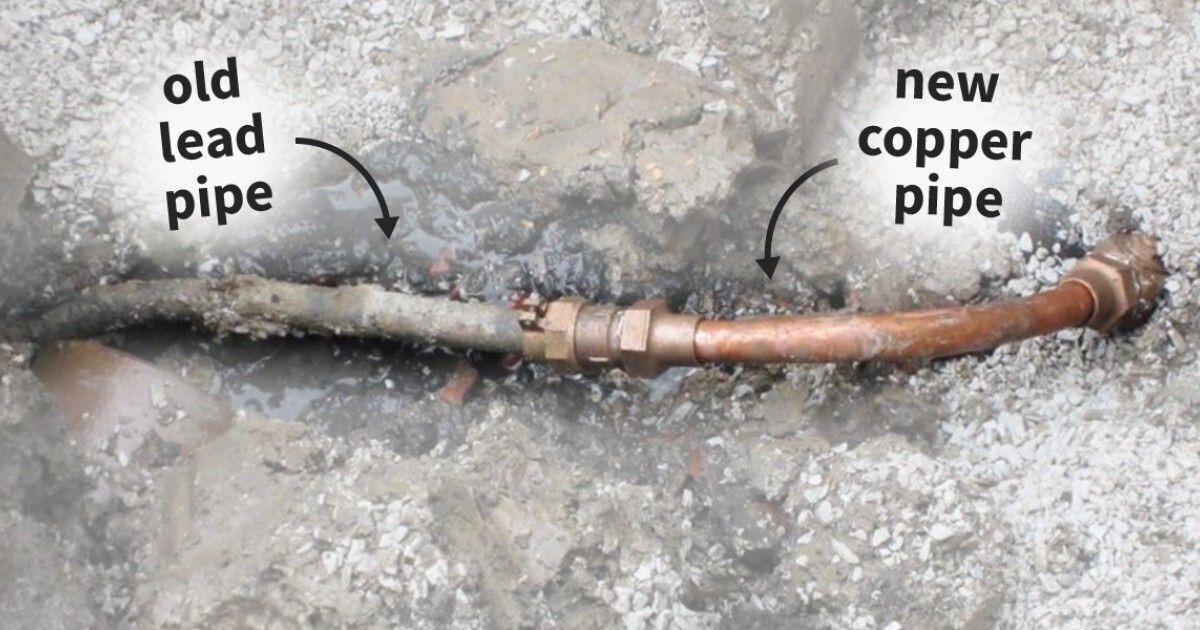
| pre-1986 plumbing | imported products | stained glass | |
| plumbing materials | batteries | stock cars |
Lead Poisoning Prevention
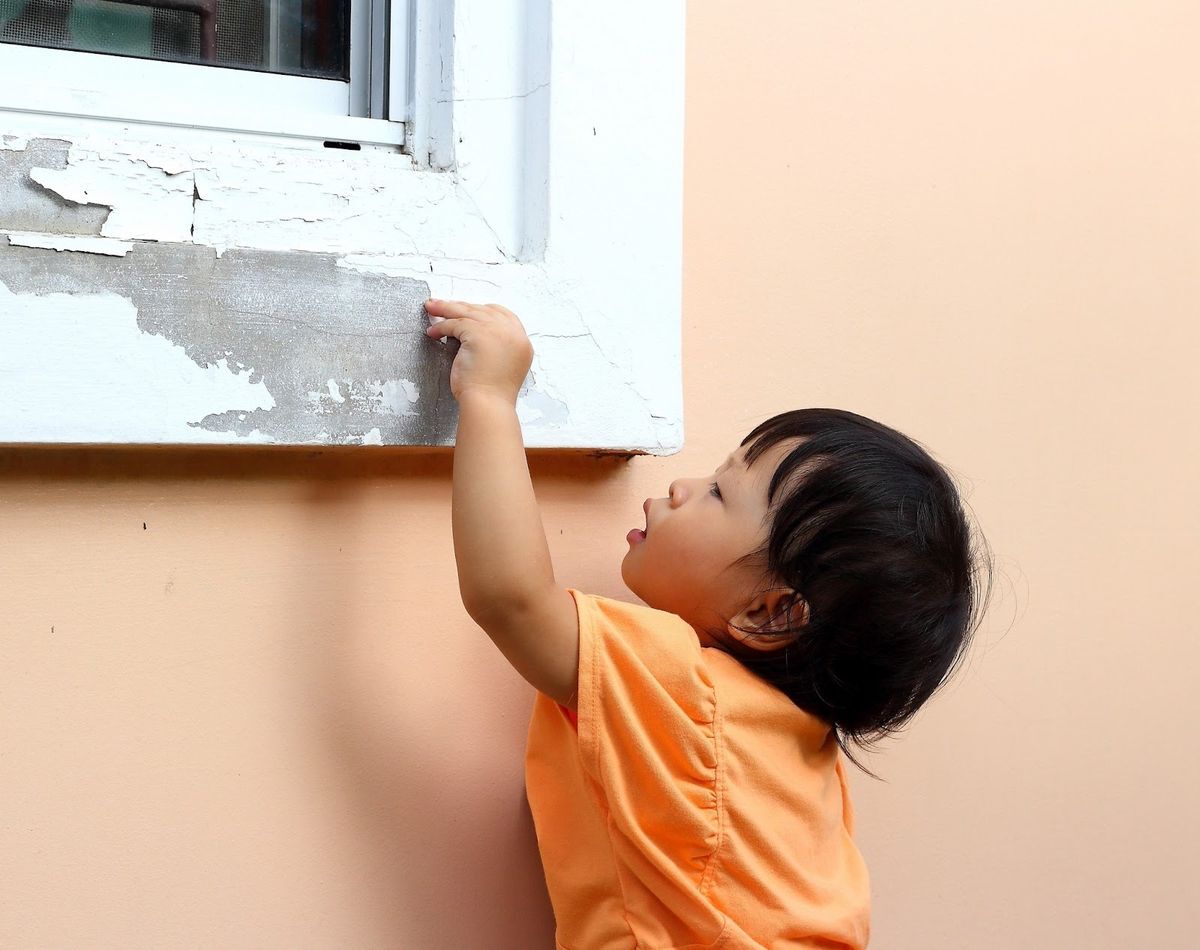
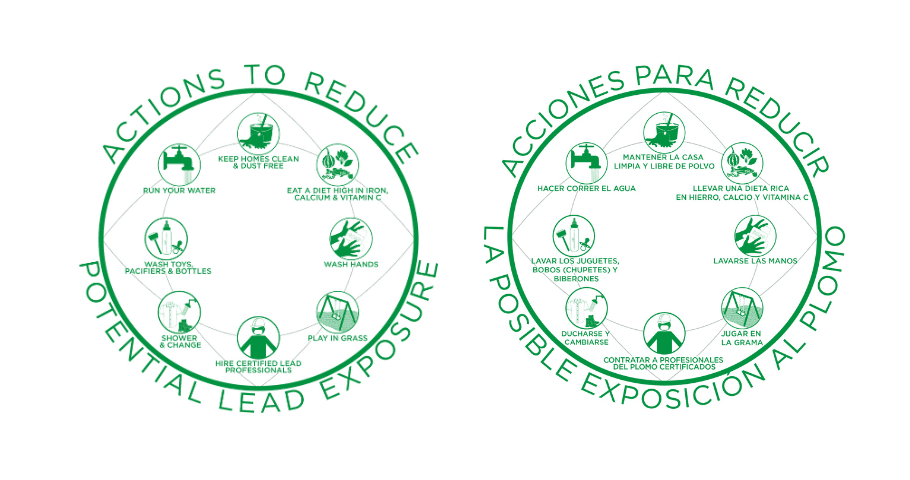
- Keep Homes Clean & Dust Free. Pre-1978 homes may contain lead paint. As the paint deteriorates, it will create toxic dust that can be inhaled or accidentally consumed.
- Eat a Diet High in Iron, Calcium & Vitamin C. These vitamins and minerals can help keep lead from staying in the body.
- Wash Hands. Lead on the hands can accidentally be consumed when playing, eating, or smoking.
- Play in Grass. Grass can help prevent contaminated dust or soil from being consumed or tracked into the home.
- Hire Certified Lead Professionals. Renovations can cause toxic lead dust if not completed by a trained professional.
- Shower & Change. If you work with lead or participate in hobbies that may contain lead, change your clothes before returning home. If possible, shower before coming home or shower as soon as you come home. Clothes potentially contaminated with lead should be washed separately from other clothes.
- Wash Toys, Pacifiers & Bottles. Items that children use should be washed regularly to remove potential lead dust.
- Run Your Water. If you believe you have lead pipes, run cold water through your tap for 30 seconds before using it.
Lead FAQs
Should my child be tested for lead?
Your child should be evaluated by their healthcare provider at 12 and 24 months old to determine if they need to be tested. If you believe your child has been exposed to lead, talk with your healthcare provider about testing now. Nebraska Blood Lead Testing Guidelines were updated in December of 2023.
Should I be tested for lead?
If you believe you have been exposed to lead, you can have your blood tested at the doctor's office. Individuals who work with lead or have hobbies that may expose them to lead should get tested regularly.
How do I know if my water is safe to drink?
The national action level (AL) for lead is 15 ppb or 0.015 mg/L. If your home is connected to public water, contact your water company and ask for a Consumer Confidence Report or check Nebraska's Drinking Water Watch. Public water is regularly tested for contaminates that may affect human health. If public water exceeds an action level (AL), the water company is required to directly notify the consumers. Yet contamination may occur once water has entered the home. Sources of lead in drinking water can be caused by lead service lines, lead goosenecks, solder, and faucets.
If you own a home with a private well, you will need to contact a certified laboratory to test your water.
- Nebraska DHHS Public Health Environmental Lab, (402)-471-2122, Price List
What do I do if my water exceeds 15 ppb or 0.015 mg/L of lead?
- Run your tap for 30 seconds with cold water to flush out lead.
- Use cold water for cooking and preparing baby formula. Lead dissolves more easily into hot water.
- Do not boil your water. Boiling water does NOT reduce lead.
- Use an alternative source of water or filter your water.
- Get tested. Talk to your doctor about getting your blood tested.
Steps to Reduce Your Exposure to Lead in Water Handout.
What water filter should I buy to remove lead from water?
Look for filters that claim lead reduction and are certified against NSF/ANSI Standard 53 or 42. The EPA's Consumer Tool for Drinking Water Filters shows detailed examples of what to look for when purchasing water filters.
Can I shower in lead-contaminated water?
Yes. Human skin does not absorb lead from water. Yet organic lead (tetraethyl lead) is more likely to be absorbed through the skin. Dermal (skin) exposure is more of a concern among individuals who work with lead.
How do I know if a product has been recalled for lead?
Sign up for recall notifications from the Consumer Product Safety Commission. For food product recalls, sign up for notifications from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
What food should I give my child to help keep lead out?
Try to eat foods that contain calcium, iron, and vitamin C.